Scaling properties of jet structures
We studied the structure of jets in proton-proton collisions at LHC energies using Monte Carlo simulations. We demonstrate that the radial jet profiles exhibit scaling properties with charged- hadron event multiplicity over a broad transverse-momentum range. Based on statistically motivated parametrizations of the jet profiles, we proposed that the scaling behavior stems from fundamental statistical properties of jet fragmentation [9]. We also observed that the charged-hadron multiplicity distributions scale with jet momentum (Fig. 1). This suggests that the Koba–Nielsen–Olesen (KNO) scaling holds within a jet. The in-jet scaling is fulfilled without MPI, but breaks down in case MPI is present without color reconnection. Our findings imply that KNO scaling is violated by parton shower or multiple-parton interactions in higher-energy collisions [10].
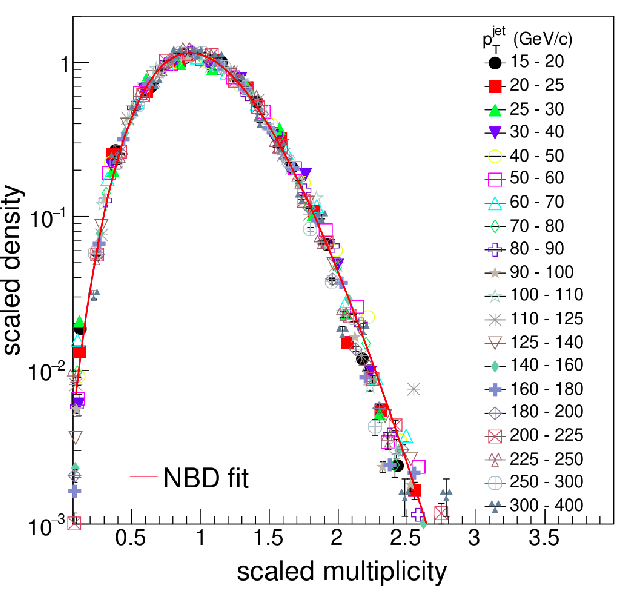
Figure 1. Multiplicity distributions in different pTjet windows, scaled by their means, with an NBD fit.
Jet substructure measurements with the CMS experiment
The internal substructure of jets reveals the mechanisms of the parton fragmentation processes. We have compared different model predictions to proton-proton collision data recorded by the CMS experiment. We investigated clusters with high rapidity along the jet axis, and found that the basic properties of these clusters are sensitive to the applied fragmentation models. We have also extended the analysis to include high pile-up runs, thus the statistical uncertainties decreased significantly. The first preliminary analysis note has been uploaded to the CERN Document Server.
[1] Gémes A, Vértesi R, Barnaföldi G G, Papp G, World Scientific: Gribov-90 Memorial Volume, arXiv:2008.08500 (2020)
[2] Vértesi R, Gémes A, Barnaföldi G G, Phys. Rev. D 103, 051503 (2021).